When an electric vehicle (EV) battery reaches the end of its road life, it doesn’t just get tossed in a landfill. In fact, what happens next is a fascinating journey of innovation, reuse, and sustainable thinking. So, where do EV batteries go when they die? Let’s unpack the life-after-life of these powerful packs.

1. Not Dead, Just Retired: The Truth About ‘Dead’ EV Batteries
A battery that’s considered “dead” for a car still retains about 70–80% of its charging capacity. While it might not be road-worthy anymore, it still holds plenty of potential for other applications. This is where second-life use comes in.

2. Second-Life Use: From Roads to Homes
Many old EV batteries are now being repurposed for energy storage — especially for solar-powered homes and businesses. Companies are building large-scale battery storage units using these retired batteries to store renewable energy for use at night or during outages.
Example: Nissan repurposes old Leaf batteries into backup power for stadiums in Japan — proving that EV batteries can live a second life long after leaving the car.
3. Recycling: The Breakdown Process
Eventually, when a battery truly reaches the end of its usability, it heads to a recycling facility. Here, key materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel are extracted for reuse.
There are three main recycling methods:
- Pyrometallurgy: High-temperature melting to recover metals.
- Hydrometallurgy: Using chemicals to dissolve and recover materials.
- Direct Recycling: Recovering battery components without breaking them down completely.
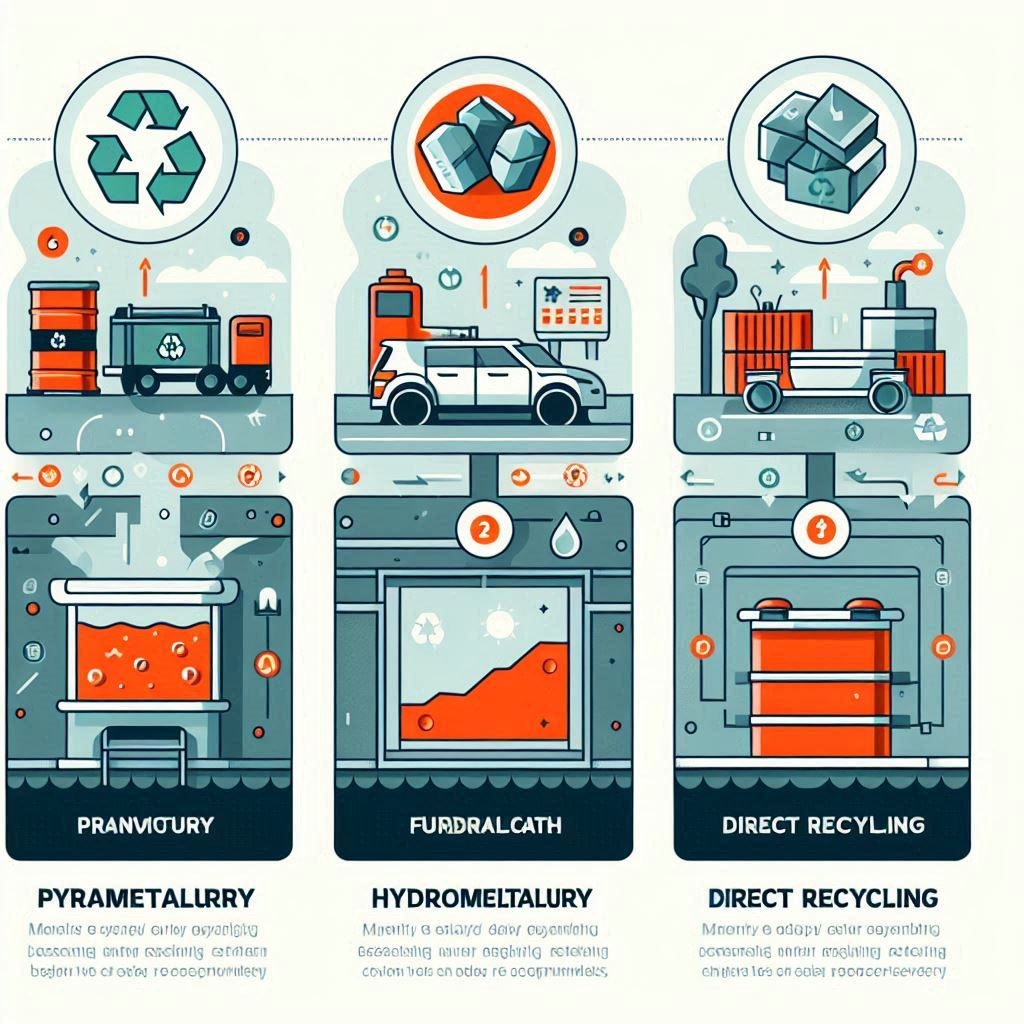
This keeps toxic waste out of landfills and reduces the demand for mining raw materials.

4. Challenges: It’s Not All Smooth Driving
While recycling tech is improving, there are still hurdles:
- Recycling rates are low globally.
- Logistics and collection systems are still developing.
- Some materials degrade and can’t be recovered efficiently.
Still, with investment and innovation, these issues are being addressed at a rapid pace.
5. The Road Ahead: Circular Economy in Action
Automakers like Tesla, GM, and Ford are investing in circular battery systems. That means designing batteries from the start to be easier to recycle, reusing materials in new batteries, and tracking them through their entire life cycle.

This shift from a linear to a circular system is essential for a sustainable EV future.
Conclusion: A Powerful Afterlife
EV batteries may retire from the road, but their story doesn’t end there. From powering homes to being reborn as new batteries, they continue to drive the clean energy movement forward. So the next time you plug in your EV, remember — its battery might be just the beginning of something much bigger.
Leave a Reply