Introduction
China’s EV supply chain is flying high! China has quietly—but powerfully—become the heartbeat of the global electric vehicle (EV) supply chain. From lithium mining to battery production and rare earth material processing, its influence is shaping the future of transportation and sustainability. In this article, we dive into how China’s EV supply chain impacts the world’s push toward a greener planet, and what it means for the future of sustainability.
1. The Powerhouse of EV Batteries

China controls over 75% of global lithium-ion battery production, making it the unrivaled epicenter of EV power solutions. Major companies like CATL and BYD are leading innovations in battery technology, providing affordable and energy-dense batteries to automakers worldwide.
2. Rare Earth Materials: A Strategic Stronghold
China is also the largest processor of rare earth elements such as neodymium and dysprosium, which are critical for EV motors. This strategic advantage enables China to maintain a crucial position in the global EV market, while also posing challenges for diversification.
3. Environmental Concerns and Green Transitions
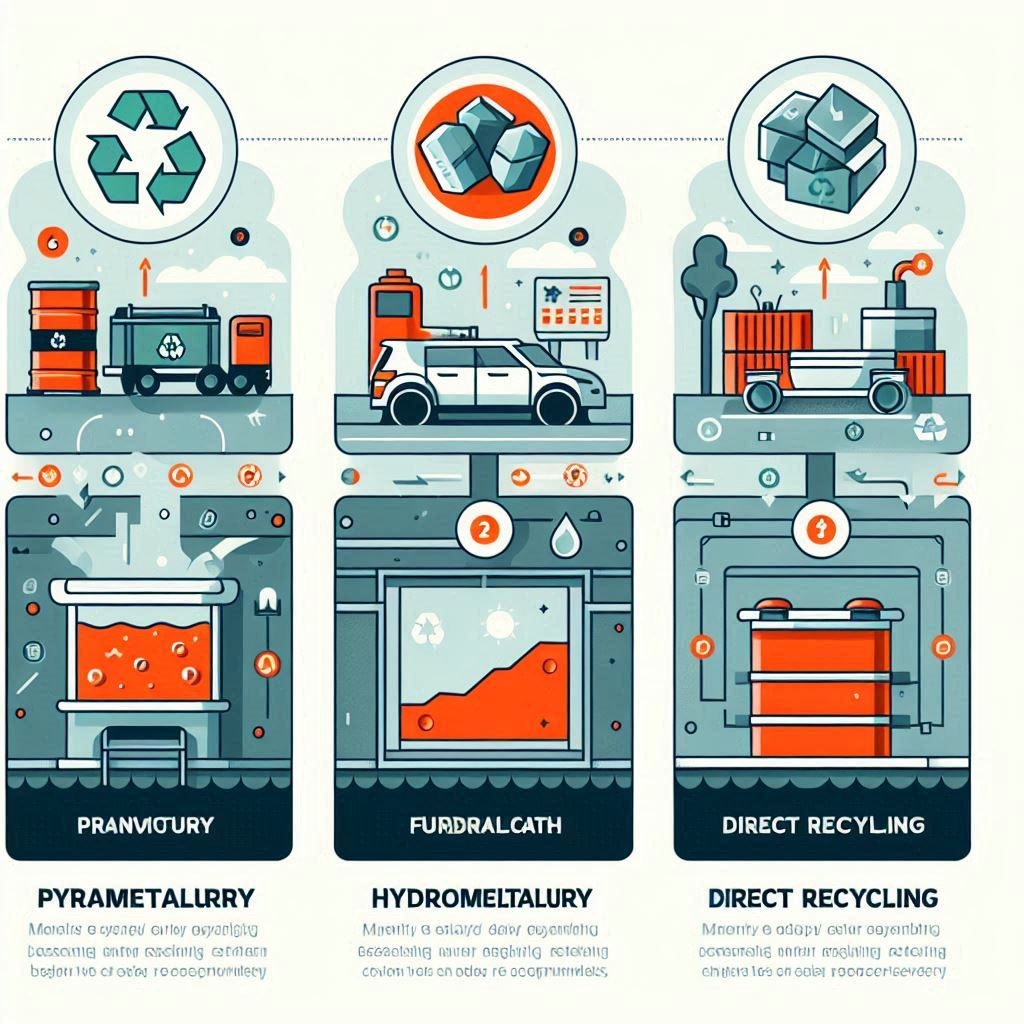
While China leads in EV infrastructure, it faces criticism over the environmental impact of mining and processing. However, green initiatives like increased recycling, stricter emissions standards, and renewable energy integration are on the rise.

4. What It Means for Global Sustainability
China’s dominance presents both opportunity and risk. On one hand, economies of scale have made EVs more affordable globally. On the other hand, supply chain dependencies raise questions about resilience and ethics. Countries are now investing in local alternatives, but catching up won’t be easy.
5. The Road Ahead
The truth is, China’s EV supply chain is a double-edged sword—accelerating global electrification while challenging other nations to rethink strategies. For a sustainable and balanced future, collaborative efforts on technology sharing, responsible sourcing, and environmental stewardship will be crucial.